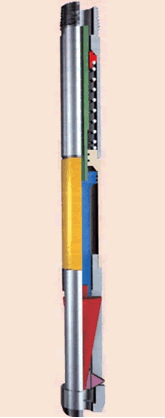
2. Hydromechanical Perforation
Application:
It is used for a secondary production formation exposure and creation
of special holes for a cement stone building up behind the production
column by drilling teams.
The PGM perforator is capable to perform two diameter opposite casing holes
of 12x40 mm at a length from 40 to 90 mm.
Action Principle:
The action principle consists in conversion of fluid hydraulic energy
into an axial movement of a stem and from the axial movement into a
radial movement of cutters.